How to Do Technical SEO for Your SaaS
To do technical SEO for your SaaS, you’ll focus on building a solid site structure, improving page speed, fixing crawl and index issues, implementing structured data, optimizing for Core Web Vitals, and ensuring every key page is easily discoverable by both users and search engines.
This means auditing your site with SaaS SEO software, like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, and PageSpeed Insights, then systematically improving issues like broken links, duplicate content, slow scripts, missing metadata, and logical internal linking.
When done right, technical SEO becomes the engine that powers all your content and link-building efforts, helping Google understand your product, your value, and why you deserve to rank. Websites that score “Good” on all Core Web Vitals metrics are 34% more likely to rank in the top 10 of Google SERPs.
Key Takeaways
- Technical setup makes your website discoverable and supports stable search rankings.
- Focus on crawling, rendering, indexing, and architecture to improve site visibility.
- Fix speed, duplicate templates, and crawl waste to stop lost traffic and demos.
- Use sitemaps, robots rules, canonicals, and redirects to protect equity.
- Balance render performance with UX to help users evaluate your product.
What Is Technical SEO for SaaS
Technical SEO for SaaS is the process of optimizing the technical foundation of your software website so search engines can easily crawl, understand, and index your pages, ultimately improving your visibility for high-intent buyers.
Unlike traditional websites, SaaS platforms often include complex product pages, dynamic content, multiple user journeys, and fast-moving feature updates that can create indexing challenges if not managed correctly. Technical SEO ensures your site architecture is clean and scalable, your pages load quickly, and your code sends clear signals to search engines about what each page represents.
This includes optimizing Core Web Vitals, implementing structured data, using proper canonicalization, managing JavaScript rendering, improving internal linking, and ensuring that every critical page, from product features to pricing, is fully accessible to both humans and bots.
When done well, technical SEO removes friction from the discovery process, allowing Google to surface your content more consistently, sending you qualified traffic that converts into trials and recurring revenue.
What Technical SEO Means For SaaS Today
A fast, crawlable website is the foundation that turns content into measurable traffic.
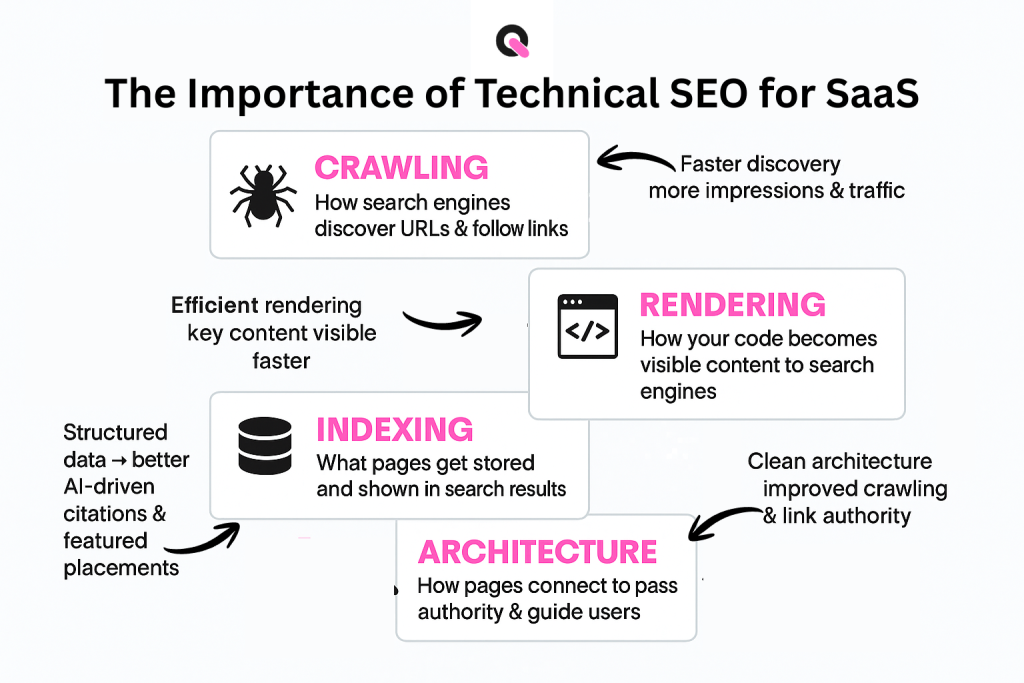
You should think of four linked layers: crawling, rendering, indexing, and architecture. Each layer must be tuned so search engines can find, understand, and surface your most important pages.
- Crawling: how bots discover URLs and follow links.
- Rendering: how code becomes visible content to an engine.
- Indexing: what gets stored and is retrievable for queries.
- Architecture: how pages connect to pass authority and help users.
When these parts work together, your content and links perform better. Clean architecture speeds crawling. Efficient rendering shows key content faster. Clear signals improve index inclusion.
Search Visibility, Traffic, And Engagement Gains
Faster discovery equals more impressions. When new pages are indexed quickly, you capture demand for timely queries and grow organic traffic.
Fixing slow pages and crawl waste reduces bounce and lifts engagement metrics. Better engagement supports improved rankings over time.
How Technical SEO Supports AI-Driven Search Citations
Structured data and correct markup make your content easier for AI-driven platforms to interpret. That increases the chance your pages are cited in answers beyond classic search results.
- Faster indexing → more impressions and qualified clicks.
- Cleaner markup → higher chance of AI citation and featured placements.
- Prioritized fixes → ensure top pages aren’t blocked or canonicalized away.
Unique Technical SEO Challenges For SaaS Companies
When your product changes often, your pages can compete or vanish before users find them. That reality creates specific risks for growing teams and their discovery channels. You need focused fixes that match rapid releases and complex product lines.
Complex Product Lines And Frequent Updates
Multiple tiers, pricing variants, and region-specific pages often create near-duplicate templates. That leads to internal competition and lost visibility if you do not consolidate or canonicalize similar content.
- Map where pricing, feature, and regional variants repeat the same content.
- Plan redirects and canonical rules for URL changes and removed features.
Data-Heavy Experiences And Site Speed Pressures
Dashboards, interactive demos, and heavy scripts slow load times. Slower pages frustrate users and reduce crawl efficiency.
Prioritize server-side rendering or partial hydration for key pages to improve perceived speed and maintain conversion paths.
Large Content Libraries And Orphaned Pages
As documentation and your blog grow, orphaned pages appear without links from main navigation. These pages remain invisible to crawlers and users.
Use internal linking governance to connect product docs, help articles, and posts to prevent fragmentation of authority and to reduce 404 and redirect chains.
| Challenge | Common Cause | Practical Fix |
| Duplicate templates | Multiple tiers, regional variants | Consolidate topics; use canonicals |
| Broken flows | Frequent URL changes, feature removals | Maintain redirect maps; limit chains |
| Slow experiences | Heavy JS, data loads | Server-side render critical pages |
| Orphaned pages | Large docs and blog archives | Enforce internal linking and audits |
Building A Crawlable, Scalable Site Architecture
Designing a site that surfaces product, pricing, and docs quickly lets discovery work for you, not against you. Map a structure that keeps core content near the homepage so both people and bots reach priority pages fast.
Flat Hierarchies, Internal Links, And Breadcrumbs
A flat hierarchy keeps important pages, product, pricing, integrations, industries, and core blog categories, within two to three clicks of the homepage.
Implement breadcrumbs that mirror your information architecture. They give users and crawlers context and make backtracking simple.
- Design hub-and-spoke links from category hubs to child pages and back to distribute authority to priority destinations.
- Separate marketing site paths from app and gated areas so crawl paths do not collide with private sections.
- Document naming rules so new pages follow predictable patterns and avoid accidental duplicates.
URL Structure Best Practices For Important Pages
Standardize URL patterns with short, descriptive slugs that reflect topics. Avoid unnecessary parameters and deep folders.
Use a category-based structure that clarifies purpose for users and improves discovery in search. Evaluate domain decisions early for internationalization or new product lines.
| Focus | Why It Matters | Quick Action |
| Hierarchy | Keeps pages accessible | Limit click depth to 2–3 |
| URLs | Help crawlers and users | Use short, descriptive slugs |
| Internal links | Distribute domain authority | Create hub-and-spoke patterns |
Crawling Essentials: Make Sure Bots Can Discover Your Pages
Map the pages must be found quickly by crawlers and humans alike. A clear discovery plan prevents important pages from being missed and saves crawl budget.
XML Sitemaps: Types, Creation, And Submission
Generate a clean XML sitemap that lists only indexable, canonical URLs. Include only the canonical version of each page and keep the file under the size limits.
- Choose the right sitemap types: standard XML, image, video, or news based on your content mix.
- Split large lists into multiple sitemap files and add a sitemap index pointing to them.
- Submit sitemaps in a console like Google Search Console to confirm processed URLs and monitor discoveries.
Robots.txt: Allow, Disallow, And Common Pitfalls
Place a robots.txt at the root of your domain to tell crawlers what to access. Use precise Disallow rules to block low-value or private areas and keep app login and admin paths excluded.
| Action | Why it matters | Quick example | ||
| Allow rendering assets | So the engine can render pages correctly | User-agent: * | Allow: /assets/css/ | Allow: /assets/js/ |
| Disallow private areas | Protect sensitive content and save crawl budget | Disallow: /admin/ | Disallow: /app/login/ | |
| Keep sitemaps aligned | Avoid listing disallowed URLs | Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml |
Validate robots changes, run a quick crawl, and check the google search console or similar tool to confirm new important pages are discovered. Keep a changelog of robots edits so you can revert unintended blockers fast.
Rendering And Performance: From Code To Core Web Vitals
Render efficiency determines whether users see value in seconds or wait through a blank screen. Faster paint times help both people and search engines evaluate your product pages quickly.
Find render-blocking assets. Defer non‑critical scripts and load analytics after primary content paints. Inline minimal critical CSS so the browser can show a usable frame fast.
- Compress text resources and serve Brotli or gzip to shrink transfer size.
- Optimize and modernize images, use responsive formats and lazy loading where appropriate.
- Reduce redirects and third‑party calls that add unpredictable latency.
Choose a rendering strategy that fits your stack: server-side rendering, static pre-render, or partial hydration for interactive pieces. Each approach can improve core web vitals while keeping demos and flows intact.
Measure against conversions. Track load metrics alongside signup or demo clicks so speed wins do not remove persuasive elements that help users convert. Cache repeat views and streamline HTML to help repeat visitors move quickly between product and pricing pages.
| Strategy | Benefit | Best for |
| Server-side render | Fast first paint and consistent render for engines | Content-heavy landing and product pages |
| Static pre-render | Low runtime cost and quick delivery | Docs and marketing pages with low interactivity |
| Hydration | Preserves interactivity with reduced JS impact | Interactive demos and complex widgets |
Indexing: Getting The Right Pages Into Search Engines
Getting the right pages into search results requires clear, consistent signals across your site. Indexing is what turns a crawl into measurable traffic and rankings.
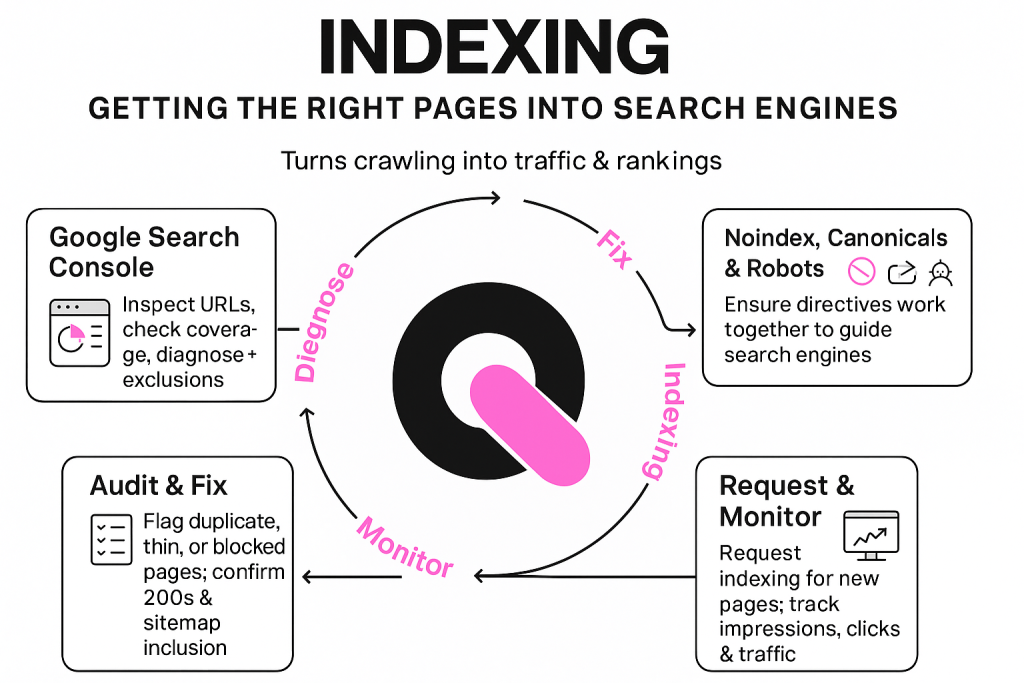
Using Google Search Console To Diagnose Indexation
Use the search console to inspect URLs, view coverage issues, and see why a page is excluded. Check status, indexing reasons, and any blocked resources that prevent rendering.
Noindex, Canonicals, And Robots Directives Working Together
Reconcile directives so they give one instruction to an engine. Noindex is for low-value or private pages. Canonical tags consolidate duplicate content to the preferred page. Robots rules should not block assets needed to render indexable pages.
- Audit index coverage and flag pages excluded for duplicate content, thin value, or blocked resources.
- Confirm important pages return 200, are in sitemaps, and canonicalize to themselves.
- Request indexing for new strategic pages and monitor their appearance in search results over time.
- Track impressions, clicks, and traffic to link indexing changes to business impact.
Fixing Duplicate Content With Canonical Tags
Duplicate pages can split authority and make it hard for your best pages to surface. Decide whether to redirect, canonicalize, or consolidate based on intent overlap, engagement history, and internal link equity.
When To Use Canonicals, 301s, Or Consolidation
Use a 301 redirect when a page is permanently moved or fully replaced. Redirects transfer existing link equity to the new URL.
Use canonical tags when variants must coexist, filters, session IDs, or tracking codes. Add self-referencing canonical tags on the master page and point variants to it.
Consolidate when content overlaps heavily. Merge similar feature or product pages into one stronger asset and update internal links to the canonical destination.
Parameter, Pagination, And Cross-Posting Scenarios
- Point parameterized URLs to a master URL with canonical tags to prevent split signals.
- Manage pagination and ensure listing pages carry primary equity and use rel=”next/prev” patterns where appropriate.
- For cross-posted blog content, set canonical tags to the original source so the source keeps priority in search results.
| Scenario | Recommended Action | Why it works | Validation |
| Moved page | 301 redirect | Preserves link equity and directs traffic | Check that new URL appears in search results |
| URL variants (params) | Canonical tag to master URL | Consolidates ranking signals | Inspect canonical header and sitemap |
| Near-duplicate features | Consolidate content | Creates a stronger, single asset | Monitor impressions and links to preferred page |
Meta Elements That Tell Search Engines What Your Pages Mean
Clear meta elements help search engines and humans decide which pages to show and click. These small signals shape how your site appears in search results and how crawlers interpret content.
Write concise, unique title tags that match query intent and help your page stand out. Keep titles focused, include the main keyword near the front, and avoid repeating the site name on every page.
- Craft meta descriptions that summarize your value and invite clicks without overpromising.
- Use a robots meta tag to control indexing and following on login, staging, or low-value pages.
- Set viewport and charset so pages render correctly on phones and desktop browsers for fast, readable content.
Eliminate duplicate titles and conflicting tags that confuse a search engine about which URL should appear. Review templates and high-impact landing pages first when auditing metadata at scale.
Example pattern you can scale: “Primary Topic — Benefit | Section”. For descriptions: “One-line value, key features, and a call to action.” Apply this across product, solutions, and blog sections.
| Element | Purpose | Quick best practice |
| Title tags | Controls SERP headline | Keep to 50–60 chars; match intent |
| Meta descriptions | Summarizes page value | Use 120–155 chars; include CTA |
| Robots meta & viewport | Index control and rendering | Use noindex where needed; declare viewport and UTF-8 |
Mobile-Friendliness And Page Experience For SaaS Users
Most buyers land on your website from a phone; design so they move fast from discovery to action.
Adopt responsive layouts that adapt to device sizes and place key CTAs, start trial, view pricing, within thumb reach. Keep page headers compact so the main content shows without extra scrolling.
Simplify navigation and use clear touch targets. Make buttons large enough to tap, and limit nested menus so users can jump between product, features, and pricing quickly.
Responsive Layouts, Touch Targets, And Minimal Pop-Ups
- Minimize intrusive overlays; if you must show a popup, ensure it is easily dismissible and does not shift content.
- Reserve space for images and embeds to avoid layout shifts when they load.
- Preload hero images and critical CSS to improve first meaningful paint on the page.
Core Web Vitals: LCP, INP/FID, And CLS Priorities
Improve Largest Contentful Paint and optimzie hero media and preloading critical assets. Reduce interaction delays (INP/FID) and defer heavy scripts and keeping the main thread free. Prevent Cumulative Layout Shift and stabilize fonts, reserving image space, and avoiding late-inserted elements.
Validate changes against key conversions so performance wins support demo requests and sign-ups, not just lab metrics.
| Issue | Impact | Quick Fix | KPIs |
| Poor LCP | Slow perceived load | Optimize hero media; preload fonts | LCP (seconds), bounce rate |
| High INP/FID | Delayed interactions | Defer non-essential JS; split bundles | INP/FID, clicks on CTAs |
| Large CLS | Visual instability | Reserve image sizes; stable ads | CLS score, session duration |
Response Codes And Redirect Logic To Protect Equity
Response codes communicate state to search engines and guide how links and pages are treated.
What 200, 301, 404, and 503 signal
200 OK means the page is healthy and indexable. Verify indexable pages return 200 to avoid soft errors that confuse crawlers.
301 Moved Permanently transfers authority. Use 301s for permanent URL changes so link equity flows to the right destination.
404 Not Found flags missing content. Restore high-value pages or redirect them to the most relevant page to reduce user frustration and crawl waste.
503 Service Unavailable signals temporary downtime. Use 503 during maintenance to preserve signals while the site is briefly offline.
Redirect maps and migration safeguards
Create a detailed redirect map before launches. List old-to-new paths, then test for loops, chains, and latency.
- Verify internal links and sitemaps point to final URLs to avoid sending crawlers through unnecessary hops.
- Apply 301s for permanent moves and avoid soft-404s that mask real issues.
- Monitor post-migration results, index coverage, impressions, and revenue-driving pages, to confirm equity retention.
- Use tags and canonical rules to prevent duplicate content and reduce indexing issues.
| Response Code | Intent | Action to Take |
| 200 | Page served and indexable | Confirm content, metadata, and sitemap inclusion |
| 301 | Permanent move; preserve links | Map old-to-new; update internal links and monitor results |
| 404 | Not found; may cause crawl waste | Restore content or redirect to relevant page |
| 503 | Temporarily unavailable | Use during maintenance; include Retry-After header |
Sitemaps And Structured Data To Enhance Discovery And SERP Appearance
Treat your sitemap as a discovery blueprint and structured data as the context that helps search engines understand your pages. A clean XML sitemap should list canonical, indexable URLs only. Add dedicated sitemaps for images and video when those media assets support your content strategy.
Use Organization markup to clarify brand details and Product markup to expose feature highlights and pricing eligibility. FAQ schema can help pages earn expanded real estate in search engine results and improve click-through rates.
- Ensure the XML sitemap only includes canonical, indexable pages and that sitemap indexes point to image and video sitemaps when needed.
- Add Organization and Product schema where appropriate so enhanced snippets can show company and product facts.
- Apply FAQ, Article, and HowTo schema to tutorials and educational content to boost eligibility for rich results.
- Keep structured data consistent with visible content, meta tags, and robots directives to avoid validation errors.
Validate before launch. Run schema checks and compare rendered page content to structured data to prevent mismatches that can invalidate enhancements. Pair schema with strong on-page content to increase the chance of incremental traffic.
| Element | Purpose | When to Use | Validation Step |
| XML sitemap | Blueprint for discovery | Main site pages, canonical URLs | Confirm sitemap in search console; no disallowed URLs |
| Image & Video sitemaps | Surface rich media | Media-heavy pages, demos, tutorials | Check media URLs and schema matches |
| Organization / Product schema | Clarify brand and product facts | Home, product, pricing pages | Use structured data tester; ensure visible attributes |
| FAQ / Article / HowTo | Enable rich results for guidance | Docs, blog posts, step-by-step guides | Validate JSON-LD and monitor rich result status |
Subdomain Vs. Subfolder: Choosing The Right Structure
Deciding between a subdomain or a subfolder influences link flow and long-term discoverability.
Subdomains can act like a separate domain in how search engines treat them. That means a subdomain may not share authority with your main site automatically.
Subfolders usually consolidate signals on the main website. Placing a blog in a folder often helps new content rank faster because links and trust accumulate on one site.
- Consider operations: separate deployments or regional stacks may justify a subdomain.
- Model internal links and navigation so users move naturally between product and educational content regardless of structure.
- Plan analytics, redirects, and governance to keep URLs stable as you grow.
| Choice | When to use | Benefit |
| Subdomain | Separate app or localized product | Isolation for different platforms |
| Subfolder | Blog or docs for the main website | Shared authority; faster organic gains |
| Hybrid | Companies with strict platform needs | Balance branding and consolidated links |
For an actionable example, map goals first: brand separation, market expansion, or easier maintenance. Then pick the structure that supports those goals while protecting search performance for your content and pages.
Technical SEO Audit Workflow, Tools, And Measurement
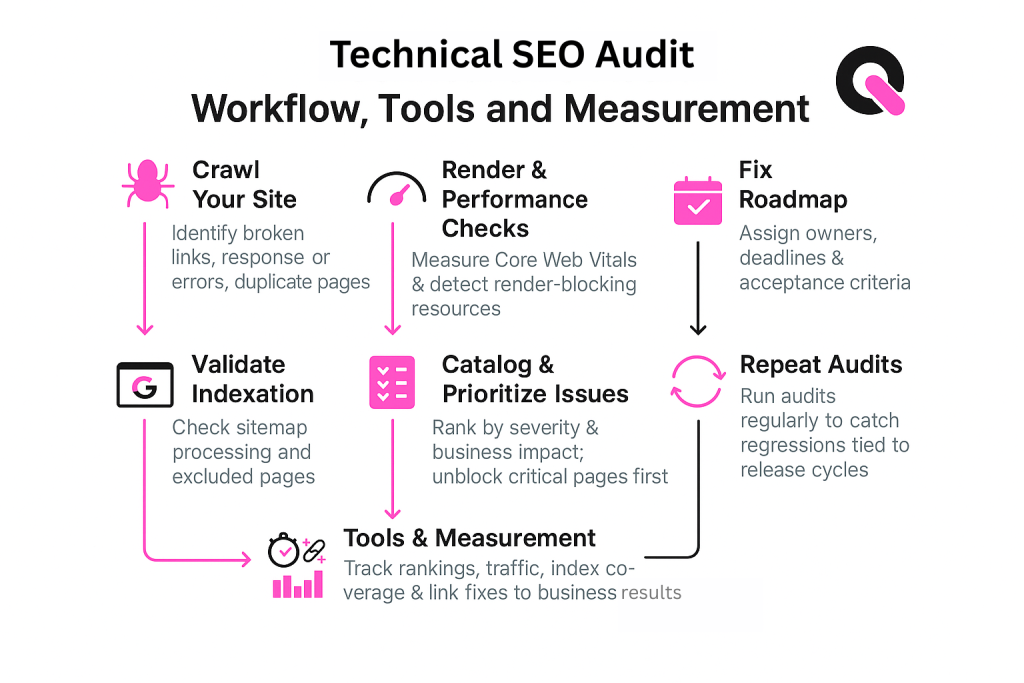
An effective SaaS SEO audit starts by crawling your site to reveal the issues that cost visibility and clicks.
Prioritized audit checklist — crawl to index
- Run a full crawl to list broken links, response-code errors, and duplicate pages.
- Perform render checks and measure Core Web Vitals to spot render-blocking resources and slow paint times.
- Validate indexation with Google Search Console: confirm sitemap processing and inspect excluded pages.
- Catalog issues by severity and business impact, unblock important pages first.
- Create a fix roadmap with owners, deadlines, and acceptance criteria.
Tools and measurement
- Use a crawler and performance tool to find problems; check the search console to request indexing for strategic pages.
- Track rankings, index coverage, and organic traffic to link fixes to business results.
- Repeat audits on a cadence tied to release cycles to catch regressions early.
🚀 How Queen of Clicks Helps SaaS Teams Win With Technical SEO
A focused audit can reveal the few site issues that block discovery and reduce demo requests. Queen of Clicks pairs engineering fixes with content and link work to drive measurable results for product-led teams.
What You Get
- Full-stack audit tailored to your needs, covering crawling, rendering, indexing, and architecture across product, pricing, and docs pages.
- Remediation plans prioritized by business impact, unblock product pages, consolidate duplicates, and speed pages without hurting conversions.
- Structured data for Organization, Product, and FAQ to improve rich-result eligibility and AI-driven citations.
- Redirect mapping and governance to protect equity during migrations, rebrands, or URL changes.
Why It Works
- We align optimization with revenue paths so internal links and hub pages send authority where it converts.
- We reduce crawl waste and index bloat so search engines focus on the URLs that matter most.
- Performance improvements are balanced with UX so faster pages still drive trials and demos.
Next Step
Ready to remove the bottlenecks holding back your organic success? Book a call with Queen of Clicks to review your website, get a prioritized action plan, and start measuring results and traffic gains.
Conclusion
When discovery and performance work together, your pages start to compound gains over time.
Technical work, clean crawling, reliable rendering, clear index signals, and purposeful architecture, lets your content reach the right audience. Fix response codes, canonical tags, sitemaps, and structured data together to protect authority and lift rankings.
Balance speed and user experience so buyers see persuasive content fast. Measure impact with coverage, ranking, and traffic changes and use governance in releases to prevent regressions.
If you want faster, more durable results, partner with Queen of Clicks to prioritize fixes and turn technical wins into measurable traffic and conversions.
FAQs
What is the first technical SEO fix a SaaS company should prioritize?
Start with crawling and indexation. If search engines can’t find or store your key pages, product, pricing, integrations, docs, nothing else matters. Run a full crawl, fix broken links, ensure all priority pages return 200, and submit a clean sitemap.
How often should a SaaS company run a technical SEO audit?
At least every quarter, or monthly if your product, pricing, and docs update frequently. Rapid releases often cause unintentional duplicates, broken links, or outdated canonical rules.
Should SaaS companies block their app or dashboard from being crawled?
Yes. App login screens, dashboards, and gated areas should be disallowed in robots.txt and set to noindex. Crawling these sections wastes crawl budget and exposes private paths.
How does technical SEO impact demo requests and sign-ups?
Fast load times and clean rendering directly improve engagement and conversion rates. When technical barriers disappear, slow scripts, blocking resources, buried pages, users reach pricing, demos, and signup flows faster.
Can poor internal linking hurt SaaS visibility?
Yes. Weak linking leaves important product and feature pages buried. A hub-and-spoke structure helps distribute authority and ensures crawlers (and users) reach converting pages within 2–3 clicks.
Should SaaS companies use structured data on product pages?
Yes. Product, Organization, FAQ, and Article schema help search engines understand your offering and improve eligibility for rich results, which boosts click-through rate and trust.
How do redirects affect technical SEO after a SaaS rebrand or migration?
Redirects protect your authority. A proper 301 map preserves backlinks and traffic, reduces 404s, and ensures both users and crawlers reach the updated version of each page without losing equity.







