SaaS International SEO: A Complete Guide
SaaS International SEO is the practice of optimizing a SaaS company’s website and content so it ranks well across multiple countries and languages, not just in a home market. It goes beyond simple translation: you adapt keywords, user intent, technical setup (like hreflang tags and URL structures), and cultural relevance so search engines understand which market and language each page serves. This ensures your product shows up in the right search results wherever your ideal users are searching.
This isn’t niche anymore; with about 70% of global search queries occurring in languages other than English, companies that ignore non-English markets are leaving the bulk of potential traffic on the table.
Key Takeaways
- Build visibility and match content to local intent and keywords.
- Follow a clear framework: choose, localize, implement, build, measure, iterate.
- Technical setup (architecture + hreflang) is required for correct targeting.
- Recurring-revenue products scale well if discoverable in local search engines.
- Use the guide’s examples and checklists to make immediate decisions.
International SEO For SaaS: What It Is And Why It Matters
Ranking well abroad requires deliberate pages, local keywords, and clear geographic signals to search engines. A product’s reach grows only when content and technical setup match the target audience and language of each market. This section defines what that actually looks like for a modern cloud product.
International SEO Definition For SaaS Companies
For SaaS companies, international SEO is the mix of strategy, technical signals, and localized content that helps a site rank in multiple countries and languages.
It includes URL structure, hreflang or equivalent tags, and landing pages that use local keywords and phrasing.
How International SEO Differs From Traditional SEO
Traditional work focuses on one market, one language, and one set of intents. Multi-market work manages multiple intents, varied search engines, and different buying journeys across countries.
That means more pages, more testing, and careful keyword mapping to each region.
What “Localization” Really Means Beyond Translation
Localization is a conversion lever. It covers tone, visuals, regulatory mentions, and UX details like currency and date formats.
When you match local intent, users face less friction and trials, demos, and signups convert better.

The Business Case For Going Global With Organic Search
Expanding organic presence in new markets reduces long-term customer acquisition costs and proves demand before large investments. Recent forecasts show strong growth: one estimate pegs the global search market at USD 22,722.03 million by 2033, while another values the market at $82.3B in 2023 with a projected $143.9B by 2030. Those figures signal that search remains a durable channel as competition rises.
Why now: market signals and economics
Organic work compounds: content assets accrue rankings and traffic over time, lowering marginal CAC. This makes organic a hedge against paid media volatility and a long-term engine for customers and product-led growth.
Tie organic efforts to revenue and pipeline
Map pages to target conversion actions by region, trial, demo, or contact sales, and set market-level objectives leaders care about, such as revenue influence, pipeline creation, or self-serve signups.
- Validate demand: use organic queries to test markets before hiring sales or signing partnerships.
- Set realistic timelines: indexing → rankings → conversions; expect phased ramps over months.
- Build a moat: localized pages and regional authority are costly for competitors to copy at scale.
| Market Goal | Primary Metric | Expected Timeline | Business Impact |
| Revenue Influence | Attributed ARR from organic | 9–18 months | Direct growth with low marginal CAC |
| Pipeline Creation | Qualified leads from organic | 6–12 months | Shortens sales cycles and informs GTM |
| Self-Serve Signups | Trial activations per market | 4–10 months | Scalable acquisition and product-led expansion |
| Market Validation | Search demand & intent signals | 1–4 months | De-risks expansion spend |
Choosing Target Markets With Data, Not Guesswork
Use your existing traffic to spot markets that already want your product. Pull country-level analytics to reveal where users and sessions are growing, even without localized pages.
Finding current demand in your existing geo traffic
Look for countries sending consistent users and engagement. Check sessions, bounce rate, and goal completions tied to trials or demos.
Evaluating market fit: competition, conversions, and adoption trends
Run simple research: use search performance tools to surface country queries and landing pages with impressions and clicks. Measure local competitors, SERP difficulty, buyer readiness, and conversion rates.
Prioritizing a “start small” rollout for faster ROI
Score each market with a simple formula: Demand × Fit × Feasibility. Pick 1–3 markets to validate templates for content, technical setup, and reporting.
- Hidden demand: countries with organic clicks but no localized content.
- Key metrics: users, sessions, engagement, conversions tied to trials/demos.
- Avoid guesswork: don’t translate broadly without data or spread resources too thin.
| Criterion | What to check | Why it matters | Action |
| Demand | Country users & search impressions | Shows latent interest | Rank markets by volume |
| Fit | Competitors & buyer readiness | Predicts conversion potential | Assess SERP difficulty |
| Feasibility | Localization effort & tooling needs | Determines speed to market | Plan 1–3 market rollouts |
| Outcome | Conversion uplift & repeatable process | Validates expansion | Scale once repeatable |
Building A Regional SEO Strategy That Can Scale
A scalable regional strategy starts with real personas and clear, time-bound goals. Treat markets as distinct audiences and build repeatable processes that link content, tech, and local input.
Defining Region-Specific Personas and Pain Points
Create 2–4 target personas per region. Capture company size, industry mix, procurement steps, and budget norms.
Example pain points vary: one market may prioritize compliance and data residency, another demands integrations and fast onboarding. Map these differences to page messaging and feature highlights.
Setting Market-Level KPIs for Traffic, Leads, and Rankings
Use measurable targets: increase organic sessions by X% in 6 months, grow non-branded share, hit top-5 rankings for Y keywords, and generate Z qualified leads.
Core KPIs:
- Organic sessions and traffic growth
- Non-branded vs branded share
- Top keyword rankings and SERP features
- Qualified leads, trial-to-paid rate, and assisted revenue
Budgeting and Resourcing Across Countries and Languages
Allocate resources by market priority and expected ROI. Concentrate spend where demand and feasibility align, and reserve capacity for ongoing iteration.
Ensure native or near-native writers, local subject-matter reviewers, technical support, and UX localization. Use templates, localization briefs, and a QA checklist to onboard new countries quickly.

SaaS International SEO Keyword Research That Matches Local Intent
Keyword research for SaaS means building keyword sets that reflect how real buyers search in each market and at every stage of the funnel. Start with separate lists per country and per language instead of translating a US list. That prevents mismatches between local phrasing and actual search behavior.
Creating keyword sets per country, language, and funnel stage
Divide keywords by funnel: problem-aware, solution-aware, product/category, comparison, alternatives, and pricing. Map each group to the page type it should feed; top-of-funnel guides, solution pages, or pricing and comparison pages.
Accounting for spelling, terminology, and idioms
Track regional spelling and terms (for example, “billing” vs “invoicing” or different verb choices in English-speaking markets). Capture idioms and local phrasing in a single reference file so writers use the preferred local term consistently.
Competitor-driven keyword gap analysis in each market
Use market-level research tools to list competitors’ top clusters and the pages that rank. Identify gaps where competitors own intent and where your product can add clearer, localized content.
Turning keyword research into a localized content roadmap
Translate keyword clusters into a prioritized roadmap: landing pages, integration pages, use-case guides, blog tutorials, and comparison content by market. Add a governance step that documents the preferred local term per concept to avoid cannibalization.
- Quick checklist: separate keyword pools, funnel mapping, spelling guide, competitor gap list, mapped content types.
| Step | Output | Why it matters |
| Country & language audit | Localized keyword lists | Matches local search patterns |
| Funnel segmentation | Page mapping per stage | Supports full buyer journey |
| Competitor gap | Target opportunity clusters | Shows where to focus content |
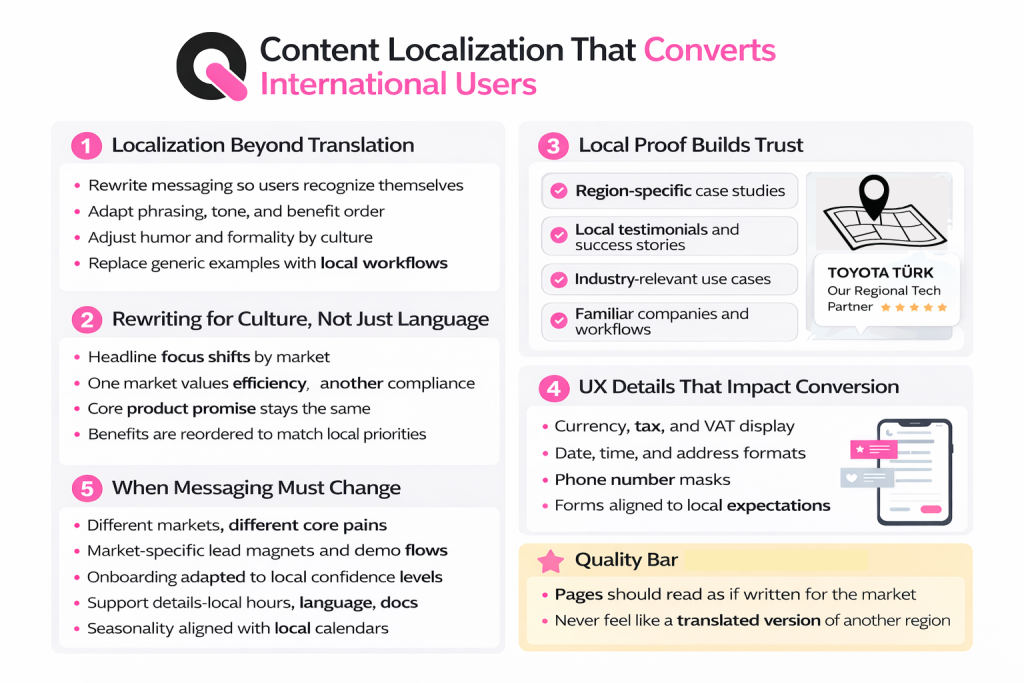
Content Localization That Converts International Users
Localization should reshape messaging so local users see themselves in the page, not a translated version of someone else’s pitch. Rewrite phrasing, tone, and benefit order to match the audience. Change humor or formality and swap examples for ones that reflect local workflows.
Rewriting for culture, not just language
Adjust headline focus by market: efficiency may lead in one place, compliance in another. Keep the core product promise, but reorder benefits to match local priorities.
Local proof: case studies and regional use cases
Add region-specific case studies, testimonials, and metrics. Use local industries and workflows so potential customers see relevant examples and trust improves.
Regional UX details that affect conversion
Small UX changes move conversions: currency and tax display, date/time formats, address fields, phone masks, and VAT hints. Ensure forms match local expectations to reduce friction.
When messaging must change by market
Change positioning when markets prioritize different pains. Offer different lead magnets, demo flows, or onboarding paths tied to local buying confidence and support needs.
- Seasonality warning: align promotions with local calendars to avoid tone-deaf campaigns.
- Support: list local hours, language options, and onboarding docs to boost trust.
- Quality bar: pages must read like they were written for the market, not merely translated.
International Site Architecture And URL Structures
Choosing the right URL model makes it easier to add languages, avoid duplicate pages, and scale fast. This decision anchors how a website signals country and language intent, how authority is shared, and how costly future migrations will be.
Country Domains, Subdomains, And Subdirectories: Tradeoffs For Scale
Three common options exist: country domains (ccTLDs), subdomains, and subdirectories. Each has clear pros and cons for SaaS-style sites.
| Option | Signal & Maintenance | When to choose |
| Country domains (ccTLD) | Strong local signal; high maintenance | Few countries, strict targeting required |
| Subdomains | Separated content; can dilute authority | Moderate markets and distinct deployments |
| Subdirectories | Shared authority; easy scaling | Many countries or many languages per site |
Consistency Rules That Prevent Future Migration Headaches
Pick one structure and apply it across the site. Consistency reduces complexity for engineers and keeps analytics clean.
- Use a single pattern for all countries and languages so every page follows the same versioning logic.
- Avoid embedding language and country in ad-hoc ways that break when you add a second language in one country.
- Ensure cross-linking and a clear switcher so users move between countries and languages without creating orphaned pages.
- Factor in engineering capacity, number of countries, and growth speed when deciding; this is part of your long-term strategy.
Finally, align the chosen architecture with your hreflang tags and other annotations so search systems can interpret each page version correctly.
Hreflang And Indexation: The Technical Backbone Of Global Visibility
Correct hreflang prevents the wrong country or language page from ranking and reduces internal competition between similar pages. For product-led websites this improves relevance, lowers bounce rates, and protects the value of localized content investments.
Where hreflang lives: head tags vs XML sitemaps
Implement hreflang in the page head when you want tight, per-page control and easy editing with your CMS. Head tags work well for small to mid-sized site clusters and for pages that change often.
Use an XML sitemap for centralized management when you have many localized pages or when engineers prefer a single source for annotations. Sitemaps scale better for large rollouts and reduce manual edits across thousands of pages.
Self-referencing and x-default best practices
Each localized page must reference itself and every alternate in the cluster. This complete set of reciprocal links creates a consistent signal for search engines and avoids broken mappings.
Use x-default to point generic visitors or language selectors to a sensible default landing page. This is especially useful for global homepages or when users arrive without a clear locale match.
Common hreflang mistakes that break rankings
- Missing return links between alternates.
- Incorrect language-region codes (use BCP 47, e.g., en-US).
- Mixing canonical and hreflang incorrectly; canonical should point within the same language cluster.
- Pointing to non-indexable URLs (noindex, blocked by robots.txt).
- Inconsistent URL formats across annotations.
| Area | Head tags | XML sitemap |
| Control | Page-level, immediate | Centralized, scalable |
| Best for | Frequent edits, small sets | Large rollouts, automated pipelines |
| Risk | CMS errors | Stale sitemap if not automated |
Indexation QA: verify each localized page is indexable, linked internally, and included in your annotations. Use site crawls and search console coverage to spot pages omitted from clusters or blocked from indexing.
Technical errors in hreflang cause mis-targeting that lowers conversions and wastes content spend, as they send users to the wrong experience. Fixing these issues protects traffic and ensures each localized version delivers its intended business impact.
Technical SEO For International Performance And User Experience
Users far from an origin server feel every extra millisecond, so global performance must be deliberate. Slow load times raise bounce rates and shrink trial or demo conversions, which is why technical SEO for SaaS plays a direct role in international growth. Treat performance as part of product-market fit for each market.
Page speed for global audiences and mobile-first expectations
Page speed matters more when many users reach your website on mobile networks. Test the critical path for the most important page templates and measure both lab and field metrics.
Keep layouts lightweight and ensure localized navigation and forms work on small screens. Mobile-first design reduces friction where mobile dominates.
Using a CDN to reduce latency across regions
A CDN caches static assets closer to regional users and stabilizes load times during traffic spikes. This cut in round-trip time improves perceived speed and conversion.
Quick wins: edge caching for images and scripts, regional POPs, and cache rules that match your release cadence.
International crawlability: internal links, facets, and duplicate paths
Crawl traps grow with scale. Language selectors, faceted navigation, and parameterized URLs can create millions of near-identical pages that waste crawl budget.
Use canonical tags aligned to localization choices and clear internal linking to preferred versions so search engines index the intended pages.
- Compress media and use responsive images.
- Minimize blocking scripts and defer noncritical code.
- Optimize web fonts and reduce font swaps.
- Measure regional performance with real-user metrics and synthetic tests.

Tie technical work back to rankings and UX: faster pages improve conversion by region, while better crawlability raises the chance your localized pages are discovered and ranked. Use performance and crawl tools regularly to catch issues early and protect traffic.
Optimizing For Search Engines Beyond Google
Regional search platforms often reward different signals than the global leader, so your pages must adapt per market.
When local engines change your approach
“Global” does not mean one search engine. Some countries rely on dominant regional platforms with unique ranking signals and user norms.
Decide whether to optimize beyond the main engine and check market share, your target audience’s search habits, and the revenue potential in those countries.
What usually differs by market
Expect variation in webmaster tools, sitemap and indexing rules, and structured data preferences. Local engines may interpret language, location, and canonical signals differently.
Content style also shifts: some markets favor short directory-style listings, others reward long-form guides or community-driven pages. Test formats before scaling.
Compliance, accessibility, and local trust
Legal and accessibility requirements can affect visibility and conversion. Regions may demand privacy notices, region-specific terms, or localized accessibility features.
Practical process to expand thoughtfully
- Implement global fundamentals first: correct architecture, hreflang clusters, and fast pages.
- Measure which markets show demand and commercial value.
- Layer market-specific tooling and content changes where data supports the investment.
| Area | Global Baseline | Market-Specific Change |
| Tooling | Search Console, sitemaps | Local webmaster tools and validation |
| Indexing | Standard XML sitemap | Custom crawl rules or submission methods |
| Structured data | Common schemas for rich snippets | Local format or markup preferences |
| Content format | Landing pages and long-form guides | Directory listings, portals, or community content |
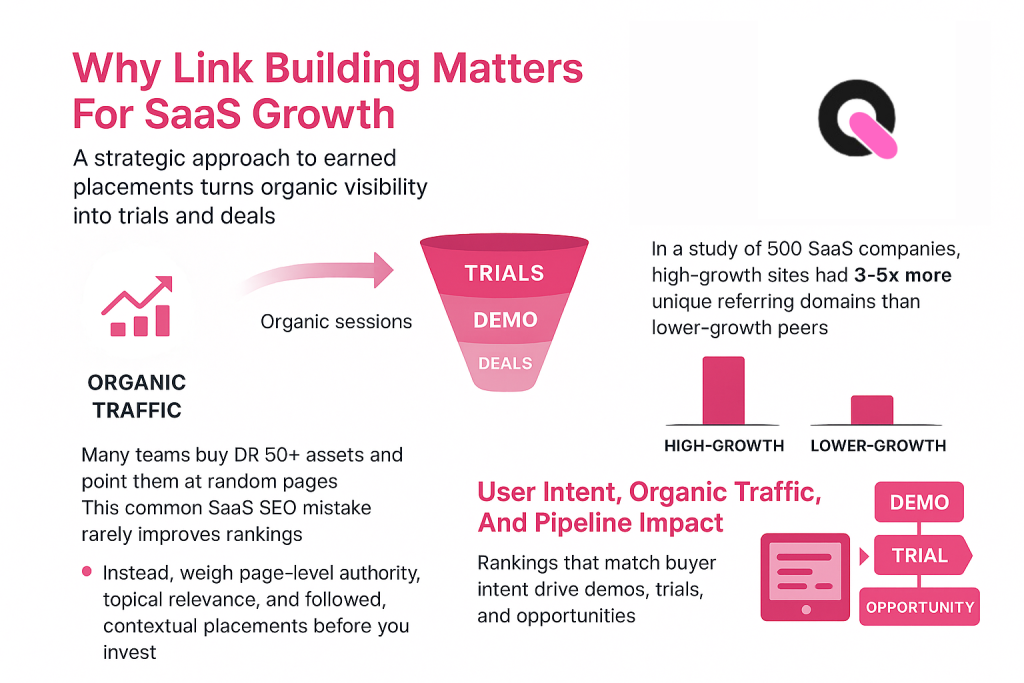
Market-Specific Link Building And Authority
Link building for SaaS is about earning trust where buyers live and work. Local links and mentions from trade groups, partner ecosystems, directories, podcasts, and events tell search systems and users that your product matters in that market.
What local authority looks like
Local authority includes backlinks from region-relevant associations, niche publications, and partner companies that local buyers follow. It also includes citations on event pages and listings where procurement teams check references.
Partnerships, digital PR, and events that earn links
Practical tactics work across markets:
- Co-marketing with local partner companies to produce localized reports and webinars.
- Digital PR: data-driven stories or benchmarks that regional press and communities share.
- On-the-ground activations: sponsoring or speaking at events and publishing post-event summaries with links.
- Contributor pieces for relevant industry sites and association directories.
Balancing global brand consistency with local outreach
Define non-negotiables: core value proposition, tone guardrails, and verified product claims. Then allow local teams to craft angles and proof points that resonate with the market.
Measure success and track link velocity, referring domains by country, and ranking lift for market-level keyword clusters. Prioritize quality relationships over volume to find lasting opportunities and better business results on your website.
Measuring International SEO Results With The Right Analytics Setup
Measure market wins, slice data by country and language so regional trends don’t disappear in global averages.
Segmenting performance for clear results
Set a minimum segmentation model: country, language, device, landing-page folder, and acquisition channel. Use consistent naming so reports align across teams.
When data is clean, you can compare traffic and users by locale rather than by blended site totals. That reveals which markets need more localization or technical fixes.
Which conversions to track
For product-led sites, prioritize trial starts, demo requests, contact-sales submissions, product-qualified actions, and paid upgrades.
Tag these events uniformly across regions so you can measure conversions per country and per language version.
Engagement diagnostics by region
Monitor bounce rate (or an engagement equivalent), scroll depth, time on page, and form completion. These metrics pinpoint localization gaps and UX friction.
Use regional funnels to see where users drop off and which pages need revised messaging or layout.
Using search performance tools and QA
Filter search-console-style reports by country to review queries, impressions, clicks, and average position for localized pages.
Check coverage and indexing errors per locale. Confirm pages are indexed, mapped to the correct locale, and not competing with each other in SERPs.
Reporting cadence and practical checks
- Weekly: operational checks for indexing, crawl errors, and major drops in traffic or conversions by country.
- Monthly: market summaries tied to business KPIs; traffic, conversions, and user engagement trends.
- Quarterly: strategic review to adjust content, technical fixes, and resource allocation.
| Focus | Metric | Why it matters | Action |
| Segmentation | Country, language, device, channel | Prevents blended averages from hiding trends | Implement naming standards and view filters |
| Conversions | Trial starts, demos, PQA, upgrades | Shows market-level revenue impact | Tag events and validate cross-region tracking |
| Engagement | Bounce, scroll depth, time, form completion | Diagnoses localization and UX issues | Run page-level audits and fix content or forms |
| Search monitoring | Queries, impressions, clicks, coverage | Surface keyword and indexing problems by country | Filter console data and resolve coverage errors |
Competitor Monitoring In Every Market You Enter
Winning abroad starts with watching how local sites structure pages and use proof elements. A focused market-level watch reveals format differences, SERP features, and trust signals that global pages often miss.
Reverse-Engineering Top Pages And SERP Features By Region
Run a quick audit on top-ranking pages: note headline intent, content depth, internal links, and local proof points like case studies or certifications.
Catalog visible SERP features, comparisons, FAQs, how-tos, and lists, then map which page types trigger them in each market.
Finding Positioning Gaps You Can Win With Better Localization
Look for pages that feel translated rather than written for the locale. They often lack local metrics, regulatory notes, or region-specific objections.
Turn those gaps into a keyword-driven content plan: build clusters that target underserved intents and match local expectations better than generic pages.
- Set a monitoring cadence per market (weekly checks for priority keywords, monthly summaries for others).
- Feed findings into the content roadmap and iterate landing pages based on what actually ranks locally.
| Focus | What to track | Outcome |
| Pages | Structure, proof, localization depth | Landing page improvements |
| SERP features | Comparisons, FAQs, templates | New content types to build |
| Movement | Keyword ranking shifts by market | Prioritized testing & updates |
Common International SEO Issues And How To Avoid Them
A surprising number of visibility problems start with literal translations and missing local trust cues. Below are three frequent issues, their impact, and clear fixes you can apply by market.
Duplicate Content Across Language Versions
Problem: Teams often clone pages or translate them word-for-word. That creates near-identical content across locales.
Impact: Search engines struggle to choose which page to rank. Traffic dilutes and pages compete instead of helping each other.
Fix: Add local context: case studies, pricing examples, and regional terms. Use hreflang and self-referencing tags. Align canonical rules so only the intended version is canonical.
Misaligned Keywords That Miss Local Search Intent
Problem: Literal translations or copied headings miss how people actually search in a market.
Impact: Pages rank weakly or attract low-quality traffic that doesn’t convert.
Fix: Re-run local keyword research, map intent to page type, and update headings and meta to match regional terminology and search patterns.
Compliance And Trust Expectations That Impact Conversions
Problem: Privacy notices, cookie flows, and procurement cues differ by market. Omitting them breaks trust.
Impact: Even with good rankings, users drop off before starting trials or demos. Conversions fall.
Fix: Publish clear local policies, show local support options, and add regional trust signals (certifications, data residency notes). Test forms and pricing to match local expectations.
- QA routine: run market audits quarterly to spot duplication, cannibalization, mistranslations, and trust blockers.
- Quick tech check: confirm hreflang clusters, canonical targets, and indexability for each localized page.
- Content check: ensure each page has unique local proof and region-specific intent mapping.

Scaling And Refining Your Global SEO Program Over Time
Treat growth as an operating system: once templates, QA checks, and reporting are stable, expansion becomes repeatable instead of chaotic. Start with 1–3 markets to prove the process, then copy the playbook to new regions.
A/B Testing CTAs, Landing Pages, And Messaging By Region
Run focused tests per market. Test CTA wording, page layout, and which proof points appear first. Different audiences respond to different commitments and social proof.
Keep tests short and measurable so you can act on results in real time and avoid long, inconclusive experiments.
Feedback Loops From Sales, Support, And Users In Each Market
Collect insights from sales calls, support tickets, and onboarding sessions. These conversations reveal objections and missing content faster than aggregate metrics.
Turn those inputs into content tasks and product copy updates. Close the loop and share outcomes with the teams that provided feedback.
Tooling And Reporting Cadences Stakeholders Will Actually Use
Invest in a few clear tools: market keyword tracking, technical audits, content QA workflows, and a simple dashboard per region. Avoid tool sprawl.
- Weekly: health checks for indexation and critical errors.
- Monthly: performance reviews of traffic, conversions, and engagement by market.
- Quarterly: strategic reviews to decide where to invest time and budget next.
| Area | What to measure | Cadence | Expected action |
| Technical health | Indexation, hreflang, crawl errors | Weekly | Fix blockers; alert engineers |
| Content performance | Clicks, CTR, engagement, conversions | Monthly | Update messaging or expand assets |
| Market signals | Sales objections, support trends | Monthly | Create targeted pages or FAQs |
| Strategy review | ROI, traffic growth, user conversion | Quarterly | Scale or pause markets |
Start small, then scale: double down on markets showing positive ROI and clear results before adding languages or countries. Repeatable templates, tidy tooling, and tight reporting save time and keep the business focused on real results.
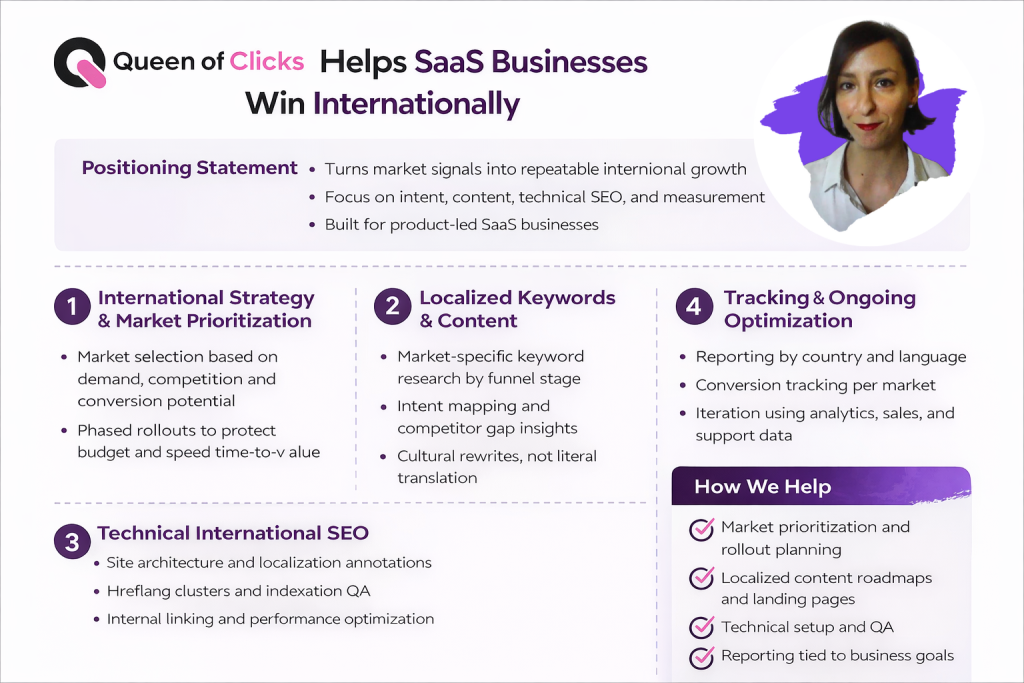
How Queen Of Clicks Helps SaaS Businesses Win Internationally
Queen of Clicks turns market signals into a repeatable growth plan for product-led businesses. We focus on intent, content, tech, and measurement so pages convert where demand already exists.
International SEO Strategy And Market Prioritization
We score markets using real demand, competitor difficulty, and conversion potential. That creates phased rollouts that protect budget and speed time-to-value.
Localized Keyword Research And Content Production
Deliverables include country and language keyword sets by funnel stage, mapped intent, and competitor gap insights. Content work uses localization briefs and cultural rewrites rather than literal translation.
Technical International SEO Implementation
We advise on site architecture, correct localization annotations, hreflang clusters, and indexation QA. Internal linking and performance tweaks help pages rank and convert across regions.
Performance Tracking, Reporting, And Ongoing Optimization
Reporting is sliced by country and language, with tracked conversions per market. Iteration cycles use data from analytics, sales, and support to refine pages and priorities.
How we help:
- Market selection based on demand signals and conversion potential to pick where to win first.
- Market prioritization models with phased rollouts to protect budget and accelerate results.
- Localized keyword research, intent mapping, and content roadmaps that guide what to build first.
- Content production: cultural rewrites, regional proof, and conversion-focused landing pages.
- Technical setup: architecture guidance, annotations, indexation QA, and performance work.
- Reporting and optimization routines that connect progress to business goals.
Next Steps
Book a call to map target markets, identify quick wins, and build an international growth plan aligned to your business objectives.
Conclusion
Winning search in new markets requires matching what people ask with pages that answer clearly and fast. Build a system that covers market selection, regional strategy, localized keyword research, culturally aligned content, accurate technical targeting, authority building, and measurement.
Localization aligns content and UX to how each audience evaluates and decides. That focus drives sustainable traffic and better conversions over time.
Keep technical non-negotiables strict: clean architecture, correct localization annotations, and indexation discipline to avoid self-competition. Start with a few markets, set market-level KPIs, review performance on a steady cadence, and iterate based on real user behavior.
If you want expert guidance to plan and execute this growth strategy, contact Queen of Clicks to map markets, tools, and time to measurable results.
FAQs
Can SaaS Companies Do International SEO in English Only?
Yes. Many B2B and SaaS buyers search in English even in non-English markets. You can validate demand, rank, and generate revenue using English pages before investing in full localization. English-first international SEO is often a smart starting phase.
How Long Does International SEO Take to Show Results for SaaS?
Early signals like impressions and indexing appear in 1–3 months. Meaningful rankings and conversions usually take 4–10 months, depending on competition, technical readiness, and content depth. Revenue impact often follows in months 6–18.
Is International SEO Worth It for Early-Stage SaaS?
It depends on traction. If you already see organic traffic or signups from other countries, international SEO can accelerate growth efficiently. If product-market fit is still unproven, focus on one or two adjacent markets rather than broad expansion.
How Many Countries Should a SaaS Company Target First?
Start with 1–3 markets. This keeps execution focused, reduces risk, and helps you build repeatable templates for content, technical setup, and reporting before scaling to additional regions.
Do You Need Separate Pricing Pages for Each Country?
Often, yes. Pricing intent varies by market due to currency expectations, taxes, purchasing power, and procurement norms. Even small changes like currency display or VAT clarity can significantly improve conversion rates.
How Do You Handle Content Updates Across Multiple Countries?
Use centralized templates with localized sections. Core product messaging stays consistent, while regional proof, terminology, and examples are updated per market. Version control and QA workflows prevent drift and inconsistency.







