GEO for SaaS Companies: A Comprehensive Guide
Generative Engine Optimization – GEO for SaaS companies is the practice of structuring your web presence, from content and technical foundations to third-party context and structured data, so that AI systems can find, verify, and cite your brand in generated answers and shortlists, not just rank it on a search engine page.GEO targets the new discovery layer: AI-powered answers that shape buying decisions before prospects ever click a link.
The shift is real: nearly one in four B2B buyers now use generative AI as much or more than traditional search when researching vendors, fundamentally changing how SaaS teams compete for attention online.
Key Takeaways
- GEO shifts discovery by placing vendors inside AI answers and summaries.
- This guide covers definitions, differences with classic SEO, and investment timing.
- SaaS needs tailored tactics because of long, complex buying journeys.
- Look for partners who prove impact with third-party validation and metrics.
- Built right, the program boosts qualified traffic, trust, and conversion.
- Content, technical foundations, and citations form the core building blocks.
Why GEO Matters for B2B SaaS Buyer Journeys
Buyer behavior is changing: 48% of B2B buyers now use AI tools during vendor research. That shift means many teams begin by asking an assistant, not typing a query into search engines.
AI overview panels reach ~1.5 billion monthly users (Q1 2025). Those overviews act as a distribution layer. Even without clicks, being cited inside an overview raises visibility and can function as a new type of ranking signal.
Nearly half of buyers use AI during vendor research
When nearly half of decision-makers turn to models first, absence becomes a pipeline risk. Treat presence in AI answers as protection for leads and revenue, not as an experiment.
AI overviews scale and awareness impact
Even a tiny share of visits from AI can drive a large share of signups. One study shows 0.5% of visits producing 12.1% of signups. That concentration means fewer clicks can yield outsized outcomes.
Why AI-referred visitors convert better
AI referrals convert ~23x higher than traditional search. Users that query assistants often include context, industry, size, budget, so referrals arrive more qualified and closer to demo decisions.
- Shift from “search then click” to “ask then shortlist” reduces exposure for teams chasing only blue links.
- Measurement must track citation visibility and recommendation share, not just raw traffic.
- Absence in shortlists means lost qualified leads before prospects land on your site.
| Metric | Observed Effect | Marketing Implication |
| 48% AI use | Large portion of buyer journeys start with AI | Prioritize mentionable, verifiable claims to earn citations |
| 1.5B monthly users | Mass distribution layer beyond clicks | Focus on consistent positioning across content and external mentions |
| 23x conversion | AI-referred visitors are highly qualified | Optimize content and signals that support shortlisting |
| 0.5% visits → 12.1% signups | Small traffic share, large signup share | Expand measurement beyond traditional traffic to capture revenue |
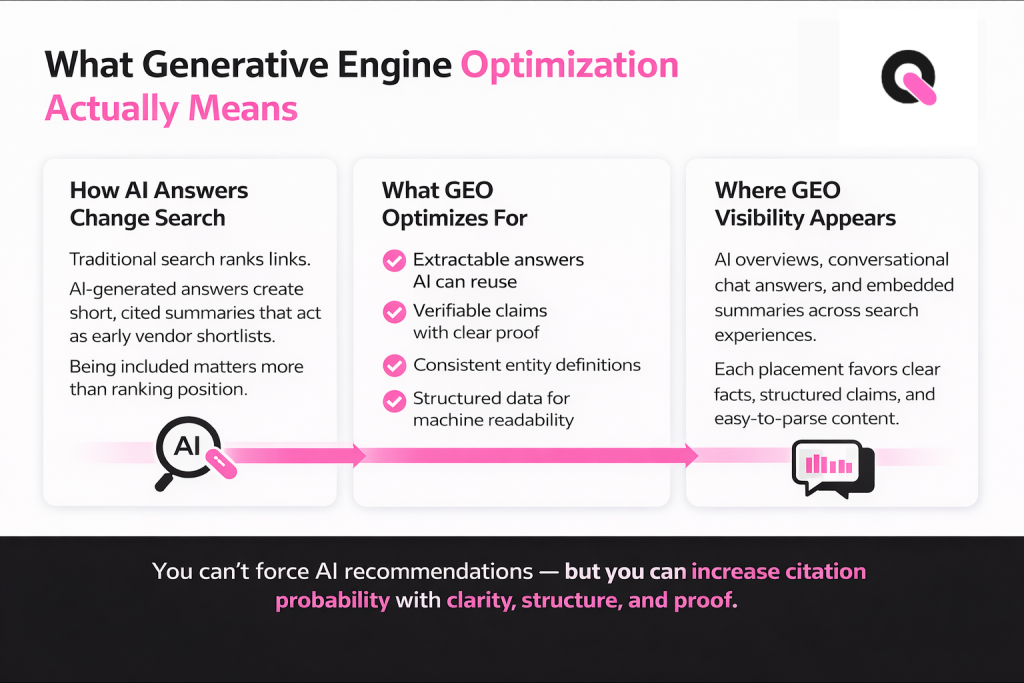
What Generative Engine Optimization Actually Means
AI-driven answers now act as an early shortlist in many B2B buying paths. Search Generative Experience optimization is the practice of making your site and wider web presence easy for models to find, verify, and cite in those answers.
How AI-powered answers differ from blue-link search engines
Classic search returns ranked links. Generated answers compress choice into a short, cited summary. That means inclusion matters more than position on a results page.
Practical takeaway: optimize passages that an engine can extract, then back them with verifiable proof so assistants can trust and reuse them.
Where this shows up: overviews, chat, and summaries
Expect citations in overview panels, conversational Q&A, and embedded summaries inside search experiences. Each placement favors clear facts, structured claims, and easy-to-parse markup.
- AI systems synthesize multiple sources and prefer extractable, evidence-backed text over vague marketing language.
- You can’t force a recommendation, but you can raise citation probability by improving entity clarity, structured data, and concise answers.
- Content strategy should prioritize answer-first pages supported by proof, not long-form thought pieces without verifiable details.
GEO vs. Traditional SEO vs. AEO
Not all visibility is the same: some tactics aim for ranked links, others aim to be cited inside assistant answers. Pick an approach by matching desired results to buyer behavior and budget.
Rankings vs. Citations: The Core Output You’re Optimizing For
Traditional SaaS SEO targets page rankings and click-throughs from search results. It still drives volume and domain authority.
Answer engine optimization focuses on being quoted or cited inside AI responses. That wins shortlists even when clicks are scarce.
Trust Signals: Links, Mentions, And Third-Party Validation
Authoritative links remain valuable, but context-rich mentions and verifiable claims now influence citation probability.
- Independent write-ups and credible coverage act as third-party validation.
- Consistent facts across sources increase the chance an assistant will cite your content.
Content Structure: “Extractable” Answers for LLM Retrieval
Make short, direct answers, clear headings, and scannable bullets. If key facts are buried, llms will skip or rewrite them incorrectly.
| Focus | Primary Output | When to Prioritize |
| Traditional SEO | Rankings & clicks | Traffic and brand discovery |
| Answer Engine Optimization | Citations & shortlists | When buyers start with assistants |
| Hybrid Approach | Both citations and rankings | Competitive markets with long sales cycles |
Decision takeaway: Build on existing SEO work, then add extractable content and third-party proof to win citations and capture AI-driven pipeline.
GEO for SaaS Companies: When It’s Worth Investing
Put the budget where AI-driven discovery is costing you real deals, not where it feels trendy. Start by validating clear signals that missing shortlists hurts your funnel. That keeps work tied to measurable outcomes and avoids reinventing classic SEO.
Signals you’re losing pipeline to AI shortlists
- Prospects say an assistant recommended competitors during calls or chat.
- Comparison and “best” pages show declining search visits while demos stall.
- Your brand drops from third-party lists and industry roundups that buyers cite.
Best-fit profiles: founder-led vs. enterprise teams
Founder-led startups need quick wins: targeted pages, tight claims, and a few high-value citations to drive early growth.
Enterprise teams require governance, scalable processes, and cross-team tooling to maintain consistent entity signals across many products and regions.
Use cases that map to revenue
Prioritize pages that capture buying intent: comparisons (“vs”, “alternatives”), category qualifiers (“for [industry]”), and “best” queries tied to integrations or pricing.
Depth matters: buyers expect methodology, proofs, and transparent criteria. Thin listicles rarely convert.
What this approach can’t fix
Optimization won’t rescue weak positioning, an unclear ICP, poor onboarding, or missing proof points. Fix fundamentals first, then scale visibility work.
- Qualification checklist: category competition, deal size, sales cycle length, and frequency of “best/alternatives” searches.
- Budget logic: invest when the cost of invisibility in assistant shortlists exceeds the cost of building lasting visibility tied to revenue results.
| Stage | Needs | Primary Goal |
| Founder-led | Quick clarity, targeted citations, tight messaging | Fast proof-of-impact and growth |
| Enterprise | Governance, scalable processes, consistent signals | Reliable, repeatable visibility and outcomes |
How AI Systems Decide What to Recommend and Cite
When models answer, they assemble identity, evidence, and context into a concise suggestion. First an engine builds an internal view of entities and retrieves candidate passages. Next it cross-checks claims against sources. Finally it synthesizes a short recommendation.
Entity Clarity: Consistent definitions of your brand, product, and category
Entity clarity means the same names, descriptions, and category labels appear across site pages, structured data, and third-party writeups. Use clear product labels and stable summaries so llms and models map you correctly.
Cross-checking behavior: Why verifiable claims win citations
Systems prefer claims backed by numbers, dated evidence, and clear scope. Include methodology, exact figures, and source links when possible. Unverified or absolute statements reduce the chance of a citation.
Context-rich mentions vs. generic backlinks
A mention that explains what you do and who you serve helps models place your brand. Generic references with no context offer less value. Quality context beats sheer volume.
| Signal | What AI likes | Action |
| Brand consistency | Stable names & structured data | Standardize copy |
| Verification | Clear numbers and dated data | Publish methods |
| Mentions | Context-rich descriptions | Seek semantic coverage |
Core GEO Building Blocks for SaaS Visibility
Start with a concise checklist that turns core visibility work into actionable tasks your marketing lead can audit this week. Focus on five layers that together improve citation probability and measurable discovery by engines and llms.
Entity Optimization Across Your Site and the Web
Standardize “what we are” statements, product names, and category terms across key pages. Repeat short definitions on landing, product, and docs pages so models map your brand consistently. Include dates and scoped claims to aid verification.
Citation Engineering and Digital PR for Semantic Mentions
Target context-rich mentions in relevant publications. Seek descriptive placements that explain who you serve and why you differ. Prioritize topical relevance, not volume.
Schema and Structured Data to Improve Machine Readability
Implement organization, product, FAQ, and breadcrumb markup. Make page intent explicit and machine-readable so assistants can extract facts without guessing.
AI-Friendly Content That Fully Answers Questions in Context
Use answer-first sections: short direct answers, constraints, examples, and “who it’s for / not for” notes. Back claims with data and sources.
Technical Foundations: Crawlability, Architecture, And JavaScript Constraints
Ensure crawlable HTML, logical internal linking, and that key content is not hidden behind heavy JavaScript. Fix accessibility and clarity first, then scale content and citations.
- Implementation order: fix accessibility & entity clarity → add structured data → publish answer-first content → pursue citation outreach.
| Layer | Primary Task | Quick Audit Item | Goal |
| Entity Optimization | Consistent names & short definitions | Check 5 pages for matching product labels | Clear mapping for engines |
| Citation Engineering | Context-rich mentions, targeted PR | List 10 relevant outlets and mention targets | Semantic visibility off-site |
| Structured Data | Product, Org, FAQ markup | Validate schema with a tester | Machine-readable facts |
| Technical Foundations | Crawlable HTML & clean architecture | Ensure important text loads without JS | Reliable indexing and extraction |
Content Strategy That Wins in AI Answers and Search
Design pages that map precise buyer prompts to clear outcomes and next steps. This aligns content with commercial intent and helps assistants pick concise, verifiable passages.
High-Intent Prompt Mapping
Map prompts to the buyer journey: problem → category → evaluation → implementation. Each stage needs distinct content that matches the question a decision-maker would ask.
Quick checklist: match queries to page intent, include scope (industry, size), and show concrete next steps.
Answer-First Page Structures
Start with a short direct answer that an engine can extract. Follow with context, criteria, trade-offs, and recommended next steps.
This structure helps both machine retrieval and human evaluation. Keep the top answer under two sentences and add scoped examples below.
Comparisons, Alternatives, and “Best Tools” Pages
Define evaluation criteria up front. State constraints (budget, integrations, team size). Explain which profile each option suits.
Avoid thin content: include methodology, update cadence, and real evidence rather than shallow listicles.
Proof-Driven Assets
Publish original data, benchmarks, and transparent calculations. Show sample methodology and date-stamped findings to increase citation likelihood.
Distribution matters: content that earns third-party mentions and citations strengthens authority and improves optimization across search and assistant channels.
- Map prompts to outcomes; prioritize pages that capture buying intent.
- Build answer-first structure with scoped examples.
- Make comparisons rigorous: criteria, constraints, and recom mendations.
- Invest in original data and clear methodology to win citations.
| Page Type | Primary Goal | Must-Have Elements | Signal to AI |
| Problem → Category | Define fit | Short answer, scope, examples | Clear entity and context |
| Evaluation / Comparison | Shortlist guidance | Criteria, trade-offs, constraints | Structured claims and evidence |
| Best Tools / Alternatives | Top recommendations | Methodology, update cadence, data | Verifiable benchmarks |
| Proof Asset | Authority & citations | Original data, transparent approach | Third-party references |
Measurement and Reporting: What to Track in a GEO Program
Start by defining what “appearing” means: where you show up, how often, and whether the context is correct. Clear operational definitions make results auditable and useful to sales and marketing.
AI visibility: operational metrics
Define visibility as three measurable items: appearance frequency, recommendation position, and correct contextual citation. Track how often you appear in an assistant list, where you rank in that list, and whether the mention includes accurate scope.
TOFU and BOFU KPIs that still work
Keep top-of-funnel signals like branded search lift, category impressions, and growth in third-party mentions. At the bottom, track demo requests, trial starts, qualified leads, and pipeline influenced by tracked referrals.
Practical cadence and attribution
Run weekly spot checks on target prompts, produce month trends, and do a quarterly review to pivot strategy. Use a blended dashboard that combines visibility metrics with traffic, leads, and revenue outcomes to handle messy mid-funnel paths.
- Require screenshots and data exports in reports so numbers are auditable.
- Use simple platforms and tools to log mentions, then tie those rows to lead records when possible.

Choosing the Right GEO Partner: Evaluation Framework for SaaS Teams
When purchasing visibility services, prioritize partners that answer technical, editorial, and measurement questions with evidence. Use a short, evidence-led scorecard to compare approach, team skills, and expected outcomes.
Technical depth: LLM crawlability, structured data, and process
Ask: how do they audit crawlability, handle JavaScript-heavy pages, implement structured data, and test llms extraction? Green flags include live audits, schema plans, and JS remediation routines.
Editorial quality: expertise-led writing vs. surface content
Check who writes and how subject-matter experts are involved. Look for a documented review process, clear claim verification, and an update cadence to keep content accurate.
Citation engineering: digital PR, unlinked mentions, and narrative control
Probe strategies to earn context-rich mentions, capture unlinked references, and correct third-party inaccuracies. Good partners pitch relevance, not volume.
Proof of results and vertical expertise
Require named case studies with steps taken, metrics, and timelines. Prioritize partners experienced with enterprise buying cycles and B2B product buying behaviors.
| Criteria | Weight | Green Flag | Red Flag |
| Technical depth | 30% | Live crawl tests, schema plan | No JS strategy |
| Editorial quality | 25% | SME writers, verification | Low-quality drafts |
| Citation engineering | 20% | Context mentions, outreach | Link-chasing only |
| Proof & vertical fit | 25% | Named case studies, enterprise wins | Anonymized claims |
Include contracting diligence: confirm scope, reporting cadence, pricing, and measurable client outcomes from day one. Use the scorecard during procurement to spot green flags and avoid common red flags.
Implementation Timeline: What Happens in the First 30, 60, and 90 Days
A clear 90-day plan helps teams turn early work into measurable visibility and pipeline. Use this roadmap to plan approvals, staffing, and weekly reporting.
Weeks 1–2: Baseline Audit
Run a fast audit of entity consistency, technical accessibility, and existing content gaps. Capture current mentions and any citation evidence models may already use.
Deliverables: inventory of pages, schema checks, and a short prioritization list that maps pages to high-intent prompts.
Weeks 3–6: Publishing and Early Optimization
Publish answer-first content focused on high-intent prompts. Apply quick technical fixes so key text is indexable and machine-readable.
Expect early citations to appear within weeks on a spotty, prompt-dependent basis. Treat these as leading indicators and iterate.
Weeks 7–12: Authority Compounding and Competitive Gains
Scale proof assets, refresh pages, and tighten internal linking. Pursue context-rich mentions and third-party validation to strengthen authority.
Monitor competitor prompts weekly and build better structured, better evidenced pages to reclaim lost visibility.
- Milestones: baseline report (week 2), early citations log (week 6), authority pulse (week 12).
- Cadence: weekly check-ins, monthly reports, and a prioritized backlog for the next quarter.
| Period | Primary Tasks | Expected Indicators |
| Month 1 | Audit entities, tech, and content | Inventory, schema fixes, priority list |
| Month 2 | Publish answer-first pages; technical optimization | Indexing, early citations, traffic lift |
| Month 3 | Refresh content; build proof assets; citation outreach | Improved ranking, steady citation growth, measured results |
Common GEO Mistakes SaaS Companies Make (And How to Avoid Them)
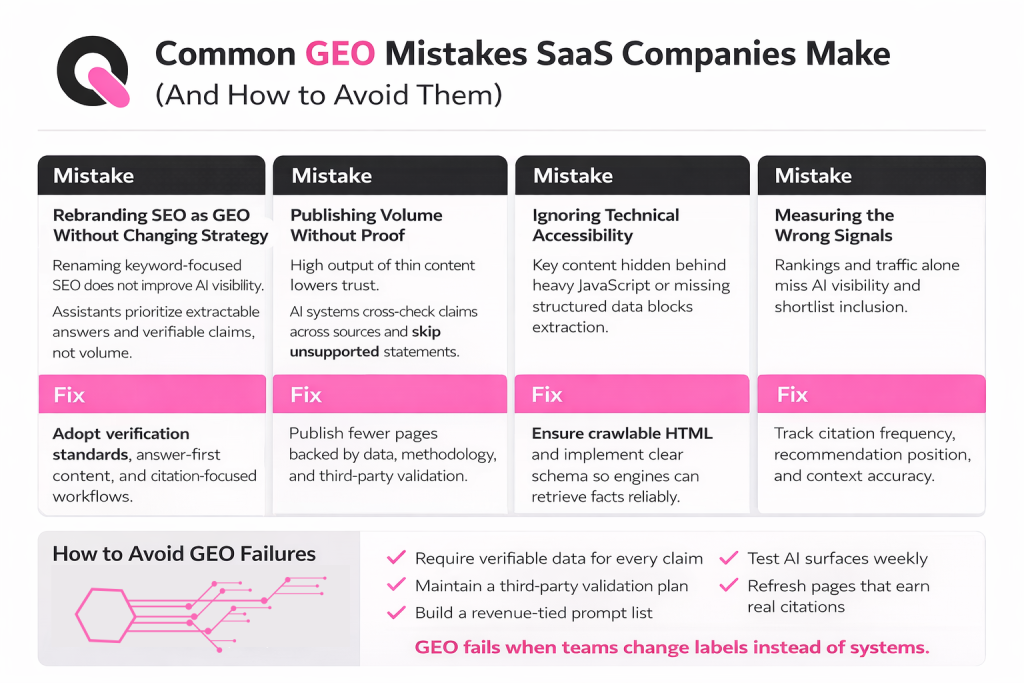
Many teams relabel existing search work but stop short of the systems and proof that drive AI citations. Calling classic SEO without changing approach is a frequent failure. That leads to the same keyword-first pages and generic link outreach with little new impact.
Rebranding SEO as GEO Without Changing Strategy
Swapping labels without new processes keeps old failure patterns. The traditional SaaS SEO checklist focuses on keywords and volume. Assistants favor verifiable claims and concise answers, so a name change alone won’t improve visibility.
Publishing Volume Without Verifiability and Third-Party Support
High output of thin content reduces trust. AI systems cross-check claims across sources. Unsupported statements and shallow pages lower citation chances and can harm brand signals.
Ignoring Technical Accessibility and Structured Data
Common technical errors block engines: important text hidden behind heavy JavaScript, blocked crawling, and missing structured data. Fix crawlability and add clear schema so models can extract facts reliably.
Measuring the Wrong Signals (Or Not Measuring AI Visibility at All)
Relying only on rankings and traffic misses AI-specific signals. Track citation frequency, recommendation position, and context accuracy. Use simple tools and monthly spot checks to validate presence in assistant surfaces.
- Prevent failures: require verifiable data for every claim and a third-party validation plan.
- Build a measurable prompt list tied to revenue and test target surfaces weekly.
- Publish, observe what gets cited, and refresh pages that earn real citations.
🚀 How Queen of Clicks Helps SaaS Companies Win GEO
Queen of Clicks helps B2B teams turn AI visibility into measurable pipeline. We combine technical work, content craft, and outreach so your product becomes an extractable, verifiable entity assistants can cite.
What You Get When You Partner With Queen of Clicks
- Baseline audit: entity mapping, crawlability checks, and content gap analysis tied to priority prompts.
- Prioritized roadmap: quick-win fixes and a 90-day plan that maps to demo and trial outcomes.
- Implementation: answer-first content, structured data, technical remediation, and citation outreach.
- Reporting: weekly spot checks and monthly visibility reports that link mentions to leads and pipeline.
How we help, in practical terms:
- Align entities and site copy so models map products clearly.
- Fix technical accessibility so key facts are retrievable.
- Publish answer-first content that converts AI-referred visitors.
- Earn credible citations and mentions that back verifiable claims.
Book a Call to Build Your GEO Roadmap
Ready to prioritize prompts, capture quick citation wins, and start a 90-day execution plan? Book a call with Queen of Clicks to get a tailored roadmap and clear next steps tied to growth and measurable results.
Conclusion
Visibility now means being quoted inside assistant answers, not only ranking in blue links. Adoption is large: AI overviews reach roughly 1.5 billion monthly users and about 48% of B2B buyers use models when they research vendors.
To win citations, prioritize consistent entity definitions, verifiable claims, clear structured data, context-rich mentions, and answer-first content. These elements improve engine optimization and answer engine optimization alike.
Invest when shortlists hurt pipeline. Map work to revenue, measure citation frequency and business KPIs, and demand transparent reporting, a clear approach, and proof tailored to platform and buying cycles.
Next step: review positioning, proof, and technical health, then build a structured roadmap to turn optimization and content work into measurable results and revenue growth.
FAQs
Is GEO only relevant if my buyers already use AI tools?
No. GEO is about future-proofing discovery. Even if AI referrals are small today, assistants already influence shortlists indirectly through summaries, comparisons, and recommendations your buyers trust. Waiting until AI is the dominant entry point usually means catching up from behind.
Does GEO replace traditional SEO for SaaS companies?
No. GEO builds on SEO. You still need crawlable pages, authority, and relevance. GEO adds an extra layer focused on being cited and recommended, not just ranked. Teams that abandon SEO fundamentals usually struggle to earn AI visibility.
How long does it take to see results from a GEO program?
Early signals (citations, mentions, assistant visibility) can appear within weeks. Pipeline impact typically shows in 60–120 days, depending on deal size, competition, and how often buyers research your category with AI tools.
Can small SaaS teams run GEO without a dedicated SEO department?
Yes, if the scope is focused. Smaller teams can prioritize:
- High-intent pages (comparisons, alternatives)
- Clear product definitions
- A handful of strong third-party mentions
Do AI engines favor big brands over smaller SaaS companies?
Not automatically. AI systems favor clear entities and verifiable claims, not brand size. Smaller SaaS companies often win citations when they publish sharper definitions, tighter scope, and stronger proof than larger competitors.
Do I need original research to succeed with GEO?
Not always, but it helps. Original data increases citation probability and trust signals. If research isn’t feasible, you still need clear methodology, scoped claims, and third-party validation to compete.

